Efficacy of Ivermectin Treatment on Disease Progression Among Adults With Mild to Moderate COVID-19 and Comorbidities
Steven Chee Loon Lim, Chee Peng Hor, Kim Heng Tay, Anilawati Mat Jelani, MMed Wen Hao Tan, Hong Bee Ker, Ting Soo Chow, Masliza Zaid, Wee Kooi Cheah, Han Hua Lim, Khairil Erwan Khalid, Joo Thye Cheng, Hazfadzila Mohd Unit, Noralfazita An, Azraai Bahari Nasruddin, Lee Lee Low, Song Weng Ryan Khoo, Jia Hui Loh, Nor Zaila Zaidan, Suhaila Ab Wahab, Li Herng Song, Hui Moon Koh, Teck Long King, Nai Ming Lai, Suresh Kumar Chidambaram, Kalaiarasu M Peariasamy, Wen Yea Hwong, Ee Vien Low, Mohan Dass Pathmanathan, Muhammad Luqman Hamzah, Yew Chung Chan, James Yau Hon Voo, Chun Fei Yap, Yon Quan Chan, Lee Kuen Vun, Kent Kian Keong Kong, Yi Fang Lim, Yee Jie Teoh, Ammar Rashidi Abdullah, Anitha Ramadas, Chee Loon Leong, Noor Hidayu Wahab, Nadiah Ismail, Ismaliza Ismail, Tung Meng Lee, Pei Jie Khoo, Sook Hui Phua, Prethivan Pillai Gopalakrishnan, Sangeetha Jaya Selan, Iswaran Ampalakan, Jen Fai Khuan, Wan Nur Farra’ain Abdul Rashid, Siti Sha’ada Zakaria, Kalaiarasan Gemini, Haslina Burahan, Thaanveer Singh Santokh Singh, Noorfarzlina Jaafar, Nor Atikah Mohd Shukri, Syaza Izhar Hisham, Sheng Hao Teow, Chit Yeh Lim, Shageetha Rajantran, Siti Izzatul Annis Kamaruddin, Izarin Izmir Izhar, Nur Syuhada Mohd Mustapha, Zulkefli Mohamad, Seri Rabiatul Nur Abu Salim, Delarina Frimawati Othman Andu, Nurnadiah Kamarudin, Karamjit Kaur Sarban Singh, Eek Poei Tay, Siti Hir Huraizah Md Tahir, Shalini Vijayasingham, Yik Zhi Kum, Peter Andrew Natarajan, Yih Harng Soh, Syed Omar Farouk Syed Alwi, Hemaarubeni Murugan, Chuan Huan Chuah, Shin Wuei Tan, Kar Nim Leong, Peng Shyan Wong, Wendy Tyng Tyng Chen, Ru Shing Ng, Yen Li Lim, Farah Nadiah Bidin, Mann Leon Chin, Han Lin Guan, Mohd Hafiz Mohamad Rasli, Rafidah Abdullah, Mohd Akmal Jamaludin, Nabilah Mohd Shohaime, Syafiqah Mohd Mansor, Ruhaizad Rasliza, Lisa Mohamed Nor, Kah Mean Thong, Balasurindiran Muniandy, Pamela Varn Teing Saw, Kah Shuen Thong, Kee Cheong Wong, V Rubini Nair Muthi, Qhairyl Iylman Ahmad Shanizza, Lavanya Jeevaraj, Ee Lin Chew, Poh Ching Huang, Jasmine Retnasamy, Philip Rajan Devesahayam, Mei San Lim, Thilagavathi Thanusia Viswanathan, Muhammad Syafiq Mahamad Azazis, Gregory Domnic, Muhammad Fursanallah Tengku, Jeanette Qiu Yi Wong, Xin Hui Choo, Ambika Nair Prabhaharan, Nur Shakirah Zaharudin, Asma Usa’diyah Abu Bakar Sayuti, Nabilah Abdul Wahid, Nurul Hasanah Saat, Nurul Huda Othman, Aisyah Ahmad Zubaidi, Nurul Miza Shasheiha Abdul Mutalib, Viknesh Dev Lekh Raj Sharma, Daleni Gunaraj, Muhammad Na'imuddin'alim Hanafi, Nurul Atiqah Embok Ungah, Muhammad Ariffadilah Mohd Zahari, Chun Lian Chaw, Jennifer Arokisamy, Puteri Amira Mohd Hassan, Ainun Jariah Ayub, Azrin Nurfarahin Zainal Abidin, Khai Sin Choong, Lee Rhui Teoh, Huan Yean Kang, Kesavathy Krishnan, Peacchaima Purusothman, Mohamad Izwan Zainol, Mei Mei Tew, Mohd Fyzal Bahrudin, Kah Chuan Lim, Sharmila Mohd Nadzir, Lavanya Narayanan, Amira Naziffa Shamsuddin, Kok Tong Tan, Shaharudeen Kamaludeen, Nur Munirah Ibrahim, Pearly Kim Aik Sim, Irdina Aminuddi, Raja Nurulain Raja Nahar Putra, Lin Ye Yah, Boon Seng Liew, Tharmini Ravi, Syarifah Nurul Ain Syed Badaruddin, Nur Suriana Mah Hassan, Zulaika Roslan, Reshaini Nadarajan, Jian-Gang Ang, Minalosani Arumugam, Kin Wei Chua, Calvin Gim Seong Ooi, Siew Huang Lee, Way Ti Ooi, Xing Yi Tang, Kunaraj Perumalu, Muhammad Hazazi Razali, Mohamad Shamirul Afiq Murat, Nor Syahirah Hamdan, Muhammad Syafiq Hamidi, Amalina Anuar, Wei Chern Ang, Chee Kong Wong, Irma Liyana Mushaddik, Shafarul Halimi Mohamed, Raja Ahmad Reza Raja Lope Ahmad, Wan Mohd Khairul Wan Zainudin, Ahmad Fikhri Mohd Zin, Sze Kye Teoh, Mohd Yusran Yusoff, Siti Norizan Abdul Rani, Mazilah Ab Rahman, Maizatul Akmal Mohd Noor, Tuan Norhafiza Tuan Mat, Mohd Khairi Othman, Mohammad Sayed Sahul Hamid Gani, Ching Zin Ngua, Andrew Kean Wei Chang, Zhun Han Wong, Andy Tze Yang Ko, Su Fui Thung, Xun Ting Tiong, Hock Hin Chua, Kiam Seong Goh, Shanthini Muthusamy, Wai Yang Loo, Thamarai Supramaniam, Rakesh Lingam, Logadharshini Chandra Kumar, Siew Theng Chun, Dariel R Selvarajah, Darshinnee Mohan Raja, One Ling Low, Prathiv Supparmaniam, Husna Ad Suhadak, Boon Cong Beh, Yi Lin Lee, Cheng Lee Ooi, Khairul Nisa' Ishak, Rozila Harun, Soon Leng Lee, Kok Soon Lee, Ji Ken Ow, Neerusha Kaisbain, Caryn Jia Wern Leong, Yun Lee Chee, Keng Long Teh, Kam Veng Chan, Kee Tat Lee, E Jinq Wong, Ibtisam Ismail, Mohd Azri Mohd Suan, Ahmad Lutfi Mohamed Yusoff, Tuan Muhd Fairuz Tuan Ismail @tuan Manah, Khairul Azmi Ibrahim, Hazfadzila Mohd Unit, Norsima Nazifah Sidek, Noraini Seman
JAMA Internal Medicine, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189
IMPORTANCE Ivermectin, an inexpensive and widely available antiparasitic drug, is prescribed to treat COVID-19. Evidence-based data to recommend either for or against the use of ivermectin are needed. OBJECTIVE To determine the efficacy of ivermectin in preventing progression to severe disease among high-risk patients with COVID-19. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS The Ivermectin Treatment Efficacy in COVID-19 High-Risk Patients (I-TECH) study was an open-label randomized clinical trial conducted at 20 public hospitals and a COVID-19 quarantine center in Malaysia between May 31 and October 25, 2021. Within the first week of patients' symptom onset, the study enrolled patients 50 years and older with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19, comorbidities, and mild to moderate disease. INTERVENTIONS Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either oral ivermectin, 0.4 mg/kg body weight daily for 5 days, plus standard of care (n = 241) or standard of care alone (n = 249). The standard of care consisted of symptomatic therapy and monitoring for signs of early deterioration based on clinical findings, laboratory test results, and chest imaging.
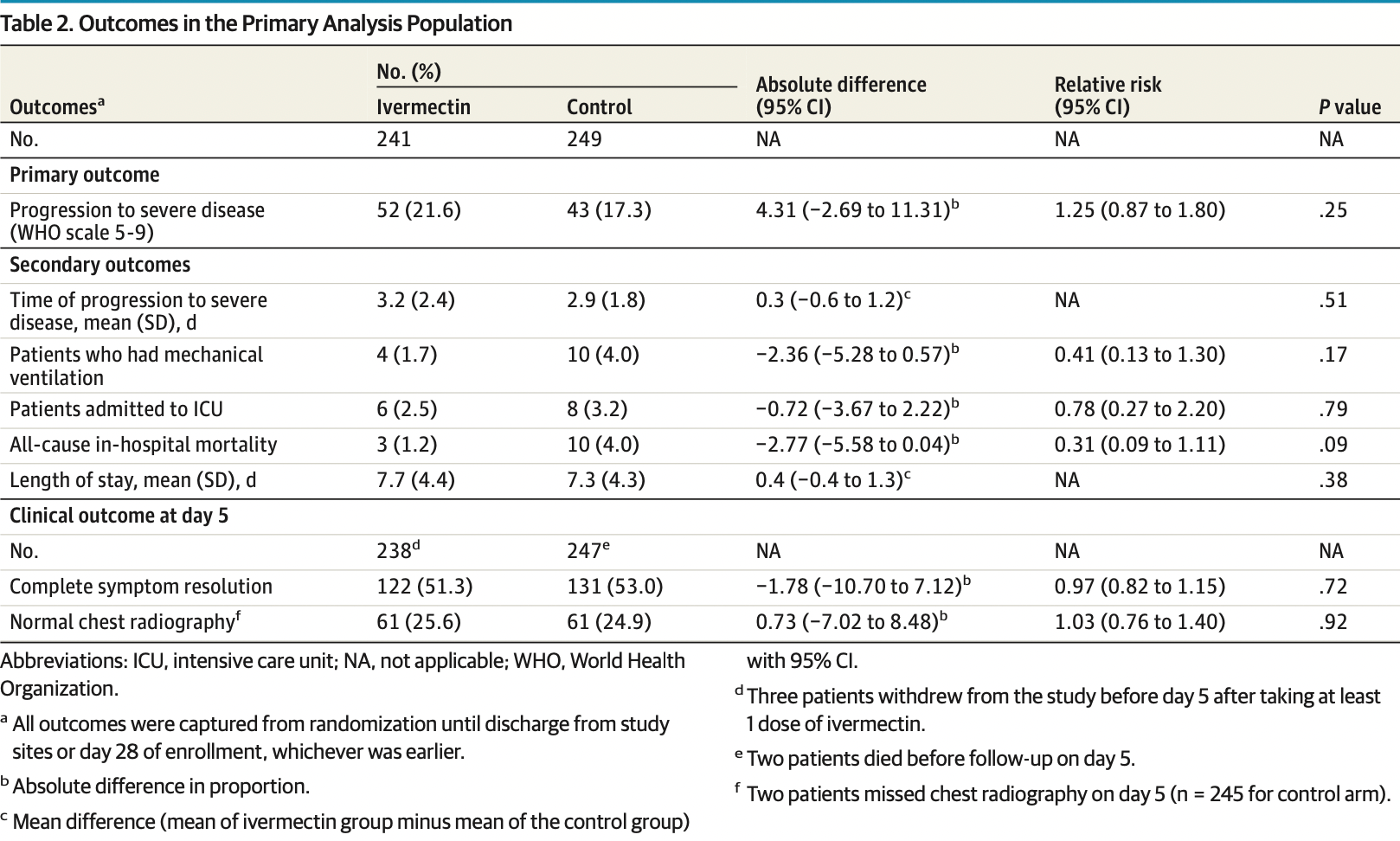
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who progressed to severe disease, defined as the hypoxic stage requiring supplemental oxygen to maintain pulse oximetry oxygen saturation of 95% or higher. Secondary outcomes of the trial included the rates of mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit admission, 28-day in-hospital mortality, and adverse events. RESULTS Among 490 patients included in the primary analysis (mean [SD] age, 62.5 [8.7] years; 267 women [54.5%]), 52 of 241 patients (21.6%) in the ivermectin group and 43 of 249 patients (17.3%) in the control group progressed to severe disease (relative risk [RR], 1.25; 95% CI, 0.87-1.80; P = .25). For all prespecified secondary outcomes, there were no significant differences between groups. Mechanical ventilation occurred in 4 (1.7%) vs 10 (4.0%) (RR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.13-1.30; P = .17), intensive care unit admission in 6 (2.4%) vs 8 (3.2%) (RR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.27-2.20; P = .79), and 28-day in-hospital death in 3 (1.2%) vs 10 (4.0%) (RR, 0.31; 95% CI, 0.09-1.11; P = .09). The most common adverse event reported was diarrhea (14 [5.8%] in the ivermectin group and 4 [1.6%] in the control group).
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE In this randomized clinical trial of high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19, ivermectin treatment during early illness did not prevent progression to severe disease. The study findings do not support the use of ivermectin for patients with COVID-19.
Conflict of Interest
Additional Contributions: The authors thank all the investigators at the 21 study sites and the Institute for Clinical Research, Ministry of Health Malaysia, for their immense contribution and support. In addition, we are grateful for the participation of the patients enrolled in this study. We also thank the members of the independent Data and Safety Monitoring Board, namely Petrick Periyasamy, MMed, National University Medical Centre, Malaysia; Lai Hui Pang, BPharm, Institute for Clinical Research, Malaysia; Mohamad Adam Bujang, PhD, Institute for Clinical Research, Malaysia; Wei Hong Lai, PhD, Institute for Clinical Research, Malaysia; and Nurakmal Baharum, BSc, Institute for Clinical Research, Malaysia. They did not receive compensation for their contribution to this study. We also thank Noor Hisham Abdullah, M Surg, Director-General of Health Malaysia, for his permission to publish this study.
References
Ahmed, Karim, Ross, A comparative study on ivermectin doxycycline and hydroxychloroquine azithromycin therapy on COVID-19 patients, Int J Infect Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, None
Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, Am J Ther,
doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, None
Drożdżal, Rosik, Lechowicz, An update on drugs with therapeutic potential for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) treatment, Drug Resist Updat,
doi:10.1016/j.drup.2021.100794Garegnani, Madrid, Meza, Misleading clinical evidence and systematic reviews on ivermectin for COVID-19, BMJ Evid Based Med. Published online,
doi:10.1136/bmjebm-2021-111678Gordon, Mouncey, Al-Beidh, Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with COVID-19
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Early treatment for COVID-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107934Guzzo, Furtek, Porras, Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects, J Clin Pharmacol,
doi:10.1177/009127002401382731Harris, Taylor, Minor, Research electronic data capture (REDCap)-a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support, J Biomed Inform,
doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010Hashim, Maulood, Rasheed, Fatak, Kabah et al., Controlled randomized clinical trial on using ivermectin with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq,
doi:10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345Hill, Garratt, Levi, Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, Open Forum Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab358Horby, Lim, Emberson, None
Khoo, Loh, Zaidan, Song, Koh et al., Statistical analysis
Kory, Meduri, Varon, Iglesias, Marik, Review of the emerging evidence demonstrating the efficacy of ivermectin in the prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19, Am J Ther,
doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377Magleby, Westblade, Trzebucki, Impact of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 viral load on risk of intubation and mortality among hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019, Clin Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa851Mahase, COVID-19: Pfizer's paxlovid is 89% effective in patients at risk of serious illness, company reports, BMJ,
doi:10.1136/bmj.n2713Mahase, COVID-19: molnupiravir reduces risk of hospital admission or death by 50% in patients at risk, MSD reports, BMJ,
doi:10.1136/bmj.n2422Marshall, Murthy, Diaz, WHO Working Group on the Clinical Characterisation and Management of COVID-19 infection. A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research, Lancet Infect Dis,
doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7Momekov, Momekova, Krolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Ivermectin as a potential COVID-19 treatment from the pharmacokinetic point of view: antiviral levels are not likely attainable with known dosing regimens, Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment,
doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959Popp, Stegemann, Metzendorf, Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Schmith, Zhou, Lohmer, The approved dose of ivermectin alone is not the ideal dose for the treatment of COVID-19, Clin Pharmacol Ther,
doi:10.1002/cpt.1889Sim, Chidambaram, Wong, Clinical characteristics and risk factors for severe COVID-19 infections in Malaysia: A nationwide observational study, Lancet Reg Health West Pac,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787Vallejos, Zoni, Bangher, Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, BMC Infect Dis,
doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Trial Investigators. REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189",
"ISSN": [
"2168-6106"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Raja Permaisuri Bainun Hospital, Perak, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Steven Chee Loon",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Kepala Batas Hospital, Penang, Malaysia"
},
{
"name": "Clinical Research Centre, Seberang Jaya Hospital, Penang, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Hor",
"given": "Chee Peng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Sungai Buloh Hospital, Selangor, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Tay",
"given": "Kim Heng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Tumpat Hospital, Kelantan, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Mat Jelani",
"given": "Anilawati",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Taiping Hospital, Perak, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Wen Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Raja Permaisuri Bainun Hospital, Perak, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Ker",
"given": "Hong Bee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Penang Hospital, Penang, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Chow",
"given": "Ting Soo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Sultanah Aminah Hospital, Johor, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Zaid",
"given": "Masliza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Taiping Hospital, Perak, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Cheah",
"given": "Wee Kooi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Sarawak General Hospital, Sarawak, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Han Hua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Kuala Lumpur Hospital, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Khalid",
"given": "Khairil Erwan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Kepala Batas Hospital, Penang, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Joo Thye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Sultanah Nur Zahirah Hospital, Terengganu, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Unit",
"given": "Hazfadzila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Sultan Abdul Halim Hospital, Kedah, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "An",
"given": "Noralfazita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Putrajaya Hospital, Putrajaya, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Nasruddin",
"given": "Azraai Bahari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Sultanah Bahiyah Hospital, Kedah, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Low",
"given": "Lee Lee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Lahad Datu Hospital, Sabah, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Khoo",
"given": "Song Weng Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Duchess of Kent Hospital, Sabah, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Loh",
"given": "Jia Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Melaka Hospital, Malacca, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Zaidan",
"given": "Nor Zaila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Tuanku Fauziah Hospital, Perlis, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Ab Wahab",
"given": "Suhaila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Research Centre, Raja Permaisuri Bainun Hospital, Perak, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Li Herng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Sungai Buloh Hospital, Selangor, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Koh",
"given": "Hui Moon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Research Centre, Sarawak General Hospital, Sarawak, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "King",
"given": "Teck Long",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, Taylor’s University, Selangor, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Lai",
"given": "Nai Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Sungai Buloh Hospital, Selangor, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Chidambaram",
"given": "Suresh Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for Clinical Research, National Institutes of Health, Selangor, Malaysia"
}
],
"family": "Peariasamy",
"given": "Kalaiarasu M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Hwong",
"given": "Wen Yea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Low",
"given": "Ee Vien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Pathmanathan",
"given": "Mohan Dass",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Hamzah",
"given": "Muhammad Luqman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Yew Chung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Voo",
"given": "James Yau Hon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Yap",
"given": "Chun Fei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Yon Quan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Vun",
"given": "Lee Kuen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Kong",
"given": "Kent Kian Keong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Yi Fang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Teoh",
"given": "Yee Jie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Abdullah",
"given": "Ammar Rashidi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ramadas",
"given": "Anitha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Leong",
"given": "Chee Loon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Wahab",
"given": "Noor Hidayu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "Nadiah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "Ismaliza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Tung Meng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Khoo",
"given": "Pei Jie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Phua",
"given": "Sook Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Gopalakrishnan",
"given": "Prethivan Pillai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Jaya Selan",
"given": "Sangeetha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ampalakan",
"given": "Iswaran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Khuan",
"given": "Jen Fai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Abdul Rashid",
"given": "Wan Nur Farra’Ain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Zakaria",
"given": "Siti Sha’ada",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Gemini",
"given": "Kalaiarasan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Burahan",
"given": "Haslina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Santokh Singh",
"given": "Thaanveer Singh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Jaafar",
"given": "Noorfarzlina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Shukri",
"given": "Nor Atikah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Izhar Hisham",
"given": "Syaza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Teow",
"given": "Sheng Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Chit Yeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Rajantran",
"given": "Shageetha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Kamaruddin",
"given": "Siti Izzatul Annis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Izhar",
"given": "Izarin Izmir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Mustapha",
"given": "Nur Syuhada",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohamad",
"given": "Zulkefli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Abu Salim",
"given": "Seri Rabiatul Nur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Othman Andu",
"given": "Delarina Frimawati",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Kamarudin",
"given": "Nurnadiah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Sarban Singh",
"given": "Karamjit Kaur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Tay",
"given": "Eek Poei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Md Tahir",
"given": "Siti Hir Huraizah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Vijayasingham",
"given": "Shalini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Kum",
"given": "Yik Zhi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Natarajan",
"given": "Peter Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Soh",
"given": "Yih Harng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Syed Alwi",
"given": "Syed Omar Farouk",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Murugan",
"given": "Hemaarubeni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chuah",
"given": "Chuan Huan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Shin Wuei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Leong",
"given": "Kar Nim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Peng Shyan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Wendy Tyng Tyng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "Ru Shing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Yen Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Bidin",
"given": "Farah Nadiah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chin",
"given": "Mann Leon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Guan",
"given": "Han Lin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohamad Rasli",
"given": "Mohd Hafiz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Abdullah",
"given": "Rafidah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Jamaludin",
"given": "Mohd Akmal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Shohaime",
"given": "Nabilah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Mansor",
"given": "Syafiqah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Rasliza",
"given": "Ruhaizad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohamed Nor",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Thong",
"given": "Kah Mean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Muniandy",
"given": "Balasurindiran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Saw",
"given": "Pamela Varn Teing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Thong",
"given": "Kah Shuen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Kee Cheong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Muthi",
"given": "V. Rubini Nair",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ahmad Shanizza",
"given": "Qhairyl Iylman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Jeevaraj",
"given": "Lavanya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chew",
"given": "Ee Lin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Poh Ching",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Retnasamy",
"given": "Jasmine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Devesahayam",
"given": "Philip Rajan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Mei San",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Viswanathan",
"given": "Thilagavathi Thanusia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mahamad Azazis",
"given": "Muhammad Syafiq",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Domnic",
"given": "Gregory",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Tengku",
"given": "Muhammad Fursanallah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Jeanette Qiu Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Choo",
"given": "Xin Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Prabhaharan",
"given": "Ambika Nair",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Zaharudin",
"given": "Nur Shakirah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Abu Bakar Sayuti",
"given": "Asma Usa’diyah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Abdul Wahid",
"given": "Nabilah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Saat",
"given": "Nurul Hasanah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Othman",
"given": "Nurul Huda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ahmad Zubaidi",
"given": "Aisyah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Abdul Mutalib",
"given": "Nurul Miza Shasheiha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lekh Raj Sharma",
"given": "Viknesh Dev",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Gunaraj",
"given": "Daleni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Hanafi",
"given": "Muhammad Na'imuddin'alim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Embok Ungah",
"given": "Nurul Atiqah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Zahari",
"given": "Muhammad Ariffadilah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chaw",
"given": "Chun Lian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Arokisamy",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Hassan",
"given": "Puteri Amira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ayub",
"given": "Ainun Jariah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Zainal Abidin",
"given": "Azrin Nurfarahin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Choong",
"given": "Khai Sin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Teoh",
"given": "Lee Rhui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Kang",
"given": "Huan Yean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Krishnan",
"given": "Kesavathy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Purusothman",
"given": "Peacchaima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Zainol",
"given": "Mohamad Izwan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Tew",
"given": "Mei Mei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Bahrudin",
"given": "Mohd Fyzal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Kah Chuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Nadzir",
"given": "Sharmila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Narayanan",
"given": "Lavanya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Shamsuddin",
"given": "Amira Naziffa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Kok Tong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Kamaludeen",
"given": "Shaharudeen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "Nur Munirah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Sim",
"given": "Pearly Kim Aik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Aminuddi",
"given": "Irdina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Raja Nahar Putra",
"given": "Raja Nurulain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Yah",
"given": "Lin Ye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Liew",
"given": "Boon Seng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ravi",
"given": "Tharmini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Syed Badaruddin",
"given": "Syarifah Nurul Ain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mah Hassan",
"given": "Nur Suriana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Roslan",
"given": "Zulaika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Nadarajan",
"given": "Reshaini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ang",
"given": "Jian-Gang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Arumugam",
"given": "Minalosani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chua",
"given": "Kin Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ooi",
"given": "Calvin Gim Seong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Siew Huang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ooi",
"given": "Way Ti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Tang",
"given": "Xing Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Perumalu",
"given": "Kunaraj",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Razali",
"given": "Muhammad Hazazi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Murat",
"given": "Mohamad Shamirul Afiq",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Hamdan",
"given": "Nor Syahirah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Hamidi",
"given": "Muhammad Syafiq",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Anuar",
"given": "Amalina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ang",
"given": "Wei Chern",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Chee Kong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mushaddik",
"given": "Irma Liyana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohamed",
"given": "Shafarul Halimi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Raja Lope Ahmad",
"given": "Raja Ahmad Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Wan Zainudin",
"given": "Wan Mohd Khairul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Zin",
"given": "Ahmad Fikhri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Teoh",
"given": "Sze Kye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Yusoff",
"given": "Mohd Yusran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Abdul Rani",
"given": "Siti Norizan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ab Rahman",
"given": "Mazilah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Noor",
"given": "Maizatul Akmal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Tuan Mat",
"given": "Tuan Norhafiza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Othman",
"given": "Mohd Khairi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Sayed Sahul Hamid Gani",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ngua",
"given": "Ching Zin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Andrew Kean Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Zhun Han",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ko",
"given": "Andy Tze Yang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Thung",
"given": "Su Fui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Tiong",
"given": "Xun Ting",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chua",
"given": "Hock Hin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Goh",
"given": "Kiam Seong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Muthusamy",
"given": "Shanthini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Loo",
"given": "Wai Yang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Supramaniam",
"given": "Thamarai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lingam",
"given": "Rakesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chandra Kumar",
"given": "Logadharshini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chun",
"given": "Siew Theng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "R Selvarajah",
"given": "Dariel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohan Raja",
"given": "Darshinnee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Low",
"given": "One Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Supparmaniam",
"given": "Prathiv",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ad Suhadak",
"given": "Husna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Beh",
"given": "Boon Cong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Yi Lin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ooi",
"given": "Cheng Lee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ishak",
"given": "Khairul Nisa'",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Harun",
"given": "Rozila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Soon Leng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Kok Soon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ow",
"given": "Ji Ken",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Kaisbain",
"given": "Neerusha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Leong",
"given": "Caryn Jia Wern",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chee",
"given": "Yun Lee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Teh",
"given": "Keng Long",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Kam Veng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Kee Tat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "E Jinq",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "Ibtisam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Suan",
"given": "Mohd Azri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohamed Yusoff",
"given": "Ahmad Lutfi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Tuan Ismail @Tuan Manah",
"given": "Tuan Muhd Fairuz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "Khairul Azmi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Mohd Unit",
"given": "Hazfadzila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Sidek",
"given": "Norsima Nazifah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the I-TECH Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Seman",
"given": "Noraini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "I-TECH Study Group",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Internal Medicine",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Intern Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-18T16:30:53Z",
"timestamp": 1645201853000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-18T15:00:32Z",
"timestamp": 1650294032000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T20:31:11Z",
"timestamp": 1712608271118
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 66,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/articlepdf/2789362/jamainternal_lim_2022_oi_220006_1649946556.24982.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "426",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi220006r1",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2100433",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1491",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi220006r2",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial.",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1637",
"issue": "10285",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ioi220006r3",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "238",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi220006r4",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate COVID-19.",
"author": "Dougan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1382",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi220006r5",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107934",
"article-title": "Early treatment for COVID-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab.",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1941",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi220006r6",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19—final report.",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1813",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi220006r7",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n2422",
"article-title": "COVID-19: molnupiravir reduces risk of hospital admission or death by 50% in patients at risk, MSD reports.",
"author": "Mahase",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "n2422",
"issue": "n2422",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ioi220006r8",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n2713",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Pfizer’s paxlovid is 89% effective in patients at risk of serious illness, company reports.",
"author": "Mahase",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "n2713",
"issue": "n2713",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ioi220006r9",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drup.2021.100794",
"article-title": "An update on drugs with therapeutic potential for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) treatment.",
"author": "Drozdzal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Drug Resist Updat",
"key": "ioi220006r10",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2020.100055",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and risk factors for severe COVID-19 infections in Malaysia: A nationwide observational study.",
"author": "Sim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health West Pac",
"key": "ioi220006r11",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro.",
"author": "Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "ioi220006r12",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines.",
"author": "Bryant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e434",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Am J Ther",
"key": "ioi220006r13",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377",
"article-title": "Review of the emerging evidence demonstrating the efficacy of ivermectin in the prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Kory",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e299",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am J Ther",
"key": "ioi220006r14",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjebm-2021-111678",
"article-title": "Misleading clinical evidence and systematic reviews on ivermectin for COVID-19.",
"author": "Garegnani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ Evid Based Med",
"key": "ioi220006r15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3071",
"article-title": "Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "López-Medina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1426",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ioi220006r16",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5",
"article-title": "Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.",
"author": "Vallejos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "635",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "ioi220006r17",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19.",
"author": "Popp",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "ioi220006r18",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"article-title": "A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research.",
"author": "Marshall",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e192",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "ioi220006r21",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208",
"article-title": "The REDCap consortium: building an international community of software platform partners.",
"author": "Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Biomed Inform",
"key": "ioi220006r22",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010",
"article-title": "Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support.",
"author": "Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "377",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Biomed Inform",
"key": "ioi220006r23",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab358",
"article-title": "Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection.",
"author": "Hill",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "ioi220006r26",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.v108.4",
"article-title": "The approved dose of ivermectin alone is not the ideal dose for the treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Schmith",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "762",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "ioi220006r27",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13102818.2020.1775118",
"article-title": "Ivermectin as a potential COVID-19 treatment from the pharmacokinetic point of view: antiviral levels are not likely attainable with known dosing regimens.",
"author": "Momekov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "469",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment",
"key": "ioi220006r28",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: a proof-of-concept randomized trial.",
"author": "Krolewiecki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "ioi220006r29",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191",
"article-title": "A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness.",
"author": "Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "ioi220006r30",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/009127002401382731",
"article-title": "Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects.",
"author": "Guzzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1122",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "ioi220006r33",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa851",
"article-title": "Impact of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 viral load on risk of intubation and mortality among hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019.",
"author": "Magleby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e4197",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "ioi220006r34",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "National Cancer Institute",
"key": "ioi220006r24",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "ioi220006r19",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. WHO advises that ivermectin only be used to treat COVID-19 within clinical trials. Accessed March 31, 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/who-advises-that-ivermectin-only-be-used-to-treat-covid-19-within-clinical-trials"
},
{
"key": "ioi220006r20",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 management guidelines in Malaysia. Ministry of Health, Malaysia. Accessed February 2, 2022. https://covid-19.moh.gov.my/garis-panduan/garis-panduan-kkm"
},
{
"key": "ioi220006r25",
"unstructured": "COVIDNOW in Malaysia. Ministry of Health, Malaysia. Accessed February 2, 2022. https://covidnow.moh.gov.my/deaths"
},
{
"key": "ioi220006r31",
"unstructured": "Abu Taiub Mohammed Mohiuddin? C, Mohammad? S, Md Rezaul? K, Johirul? I, Dan? G, Shuixiang? H.? A comparative study on ivermectin doxycycline and hydroxychloroquine azithromycin therapy on COVID-19 patients.? Research Square. 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ioi220006r32",
"unstructured": "Hashim? HA, Maulood? MF, Rasheed? AM, Fatak? DF, Kabah? KK, Abdulamir? AS. Controlled randomized clinical trial on using ivermectin with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq.? medRxiv. 2020. doi:10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345?"
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {
"has-review": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.3410/f.741660542.793591932",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2789362"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [
"The I-TECH Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Efficacy of Ivermectin Treatment on Disease Progression Among Adults With Mild to Moderate COVID-19 and Comorbidities",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "182"
}