Safety and Efficacy of a MEURI Program for the Use of High Dose Ivermectin in COVID-19 Patients
Marcos Alejandro Mayer, Alejandro Krolewiecki, Alejandro Ferrero, Marcelo Bocchio, Juan Barbero, Marcos Miguel, Ariel Paladini, Carlos Delgado, Juan Ramón Ojeda, Claudia Elorza, Ana Bertone, Pedro Emanuel Fleitas, Gustavo Vera, Mario Rubén Kohan
Frontiers in Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.813378
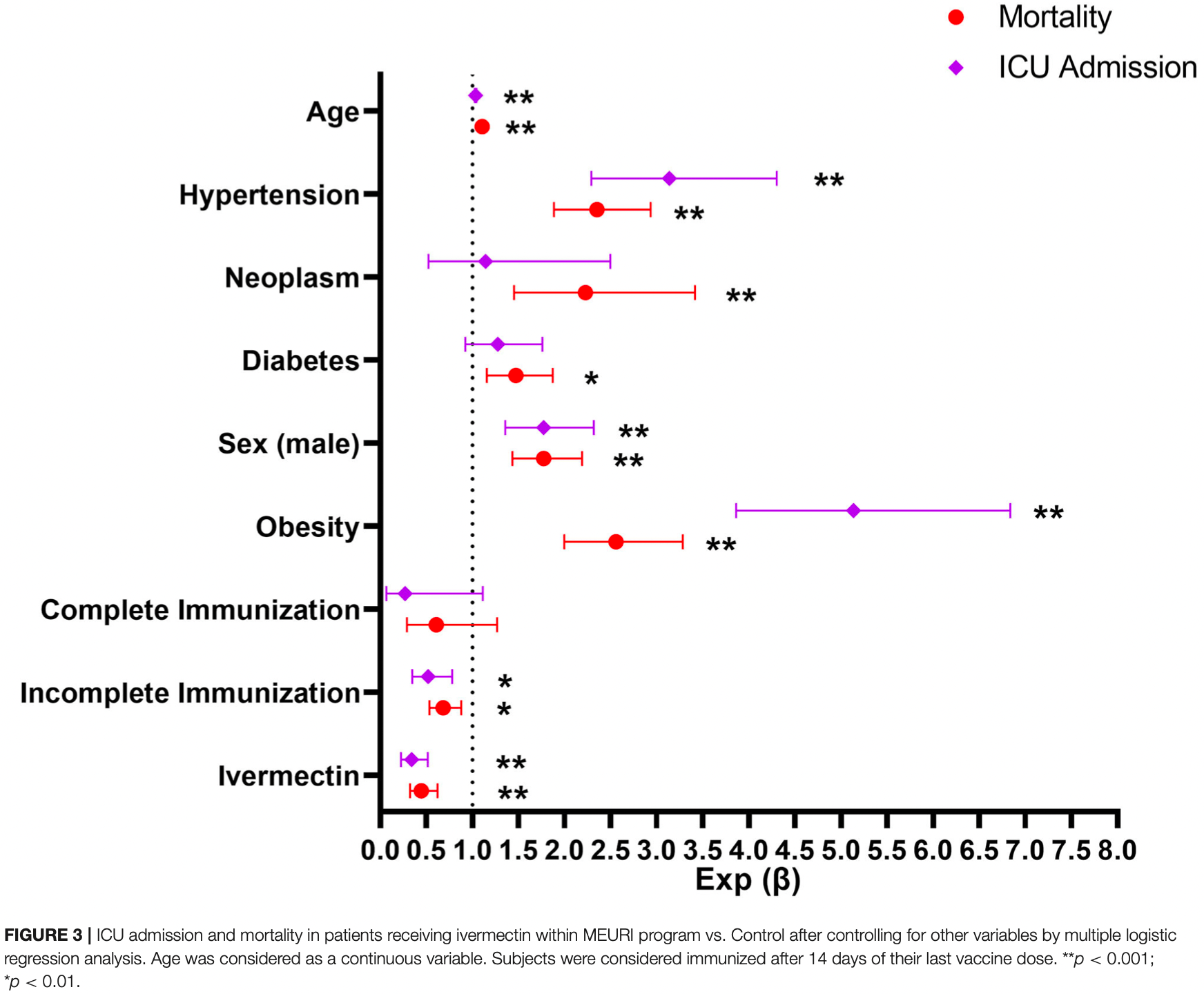
Background: In the absence of antiviral alternatives, interventions under research for COVID-19 might be offered following guidelines from WHO for monitored emergency use of unregistered and experimental interventions (MEURI). Ivermectin is among several drugs explored for its role against SARS-CoV-2, with a well-known safety profile but conflicting data regarding clinical utility for COVID-19. The aim of this report is to inform on the results of a MEURI Program of high-dose ivermectin in COVID-19 carried out by the Ministry of Health of the Province of La Pampa, Argentina. Methods: COVID-19 subjects, within 5 days of symptoms onset were invited to participate in the program, which consisted in the administration of ivermectin 0.6 mg/kg/day for 5 days plus standard of care. Active pharmacosurveillance was performed for 21 days, and hepatic laboratory assessments were performed in a subset of patients. Frequency of Intensive Care Unit (ICU) admission and COVID-19-related mortality of subjects in the ivermectin intention to treat group were compared with that observed in inhabitants of the same province during the same period not participating in the program. Results: From 21,232 subjects with COVID-19, 3,266 were offered and agreed to participate in the ivermectin program and 17,966 did not and were considered as controls. A total of 567 participants reported 819 adverse events (AEs); 3.13% discontinued ivermectin due to adverse events. ICU admission was significantly lower in the ivermectin group compared to controls among participants ≥40 year-old (1.2 vs. 2.0%, odds ratio 0.608; p = 0.024). Similarly, mortality was lower in the ivermectin group in the full group analysis (1.5 vs. 2.1%, odds ratio 0.720; p = 0.029), as well as in subjects ≥ 40 year-old (2.7 vs. 4.1%, odds ratio 0.655; p = 0.005). Conclusions: This report highlights the safety and possible efficacy of high dose ivermectin as a potentially useful intervention deserving public health-based consideration for COVID-19 patients.
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Provincial Ethics Committee of La Pampa, and participating individuals provided written informed consent. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors would like to acknowledge the authorities of the Government of the Province of La Pampa, Argentina, for their support, and to the Ivermectin Monitored Intervention program collaborators: María Alejandra Ramallo; Andrea Barbero; Liliana Torres; Nadia Paola Andresco Soto; Lucía Martín; Analisa
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Publisher's Note: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. Copyright © 2022 Mayer, Krolewiecki, Ferrero, Bocchio, Barbero, Miguel, Paladini, Delgado, Ojeda, Elorza, Bertone, Fleitas, Vera and Kohan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in..
References
Abdala, None
Alfonso, Gastón, Jouly, None
Andrea, None
Arroyo, None
Astesano, Baez, Ulivetti, None
Barboza, None
Barra, None
Barrionuevo, None
Barrionuevo, None
Bessone, Hernandez, Tagle, Arrese, Parana et al., Drug-induced liver injury: a management position paper from the Latin American Association for Study of the liver, Ann Hepatol,
doi:10.1016/j.aohep.2021.100321Biber, Mandelboim, Harmelin, Ram, Shaham, Favorable outcome on viral load and culture viability using Ivermectin in early treatment of non-hospitalized patients with mild COVID-19 -A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.05.31.21258081Bissio, Allara, Guerrero, None
Bramante, None
Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Mitchell et al., Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, Am J Ther,
doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001442Burgahrtd, Puglie, None
Calo, None
Cappozi, Vanesa, None
Carasay, None
Ceferino, None
Cervellini, Soto, Soto, None
Chaccour, Casellas, Blanco-Di Matteo, Pineda, Fernandez-Montero et al., The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with nonsevere COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial, EClinicalMedicine,
doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720De Los Santos, None
De, Prida, None
Delfino, None
Díaz, Macayo, None
Edwards, Dingsdale, Helsby, Orme, Breckenridge, The relative systemic availability of ivermectin after administration as capsule, tablet, and oral solution, Eur J Clin Pharmacol,
doi:10.1007/BF00637608Elias, Fernando, None
Ester, Carla, Morales, Marsollier, Mariné del Valle Plizzo
Fischman, None
Fritz, Morris, Richler, Effect size estimates: current use, calculations, and interpretation, J Exp Psychol Gen,
doi:10.1037/a0024338Furik, Baizero, None
Galarza, None
Garro, Santiago, None
Gimenez, None
González, Hermua, None
Guerbilli, None
Gutierrez, None
Heidary, Gharebaghi, Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen, J Antibiot,
doi:10.1038/s41429-020-0336-zHernandez, None
Hill, Garratt, Levi, Falconer, Ellis et al., Expression of concern: "meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, Open Forum Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab394Jorja, Daniel, None
Julia, None
Kow, Hasan, Pitfalls in reporting sample size calculation across randomized controlled trials involving ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19, Am J Ther,
doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001441Kredes, None
Krolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Travacio, Valentini et al., Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: a proof-of-concept randomized trial, EClinicalMedicine,
doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959Leguizamon, García, None
León, None
Lluch, None
Londero, None
Luft, None
López, None
López-Medina, López, Hurtado, Dávalos, Ramirez et al., Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, J Am Med Assoc,
doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071Maison, None
María, Martin, Tabares, Godoy, Minudri, None
Mas, Carrizo, None
Matamoros, Sanchez, Gabrie, Juarez, Ceballos et al., Efficacy and safety of albendazole and high-dose ivermectin coadministration in schoolaged children infected with Trichuris trichiura in Honduras: a randomized controlled trial, Clin Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/cid/ciab365Mendoza, None
Mercado, Ortiz, None
Moline, Whitaker, Deng, Rhodes, Milucky et al., Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in preventing hospitalization among adults aged ≥65 years -COVID-NET, 13 states, Morb Mortal Wkly Rep,
doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7032e3Monarde, Rojas, Balsa, None
Morales, None
Moran, Abdala, None
Natividad, None
Navarro, Camprubí, Requena-Méndez, Buonfrate, Giorli et al., Safety of high-dose ivermectin: a systematic review and metaanalysis, J Antimicrob Chemother,
doi:10.1093/jac/dkz524Neil, Fenton, Kow, Hasan, Popp et al., Bayesian hypothesis testing and hierarchical modeling of ivermectin effectiveness, Am J Ther,
doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001450Padhi, Pati, Panda, Effect of ivermectin in the treatment of COVID-19: a trial sequential analysis highlighted the requirement of additional randomized controlled trials, Clin Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/cid/ciab692Puglie, María, None
Pérez, Bustos, None
Quiroga, None
Quiroga, Silvia Romera, None
Ramos, None
Redel, Baigorria, None
Renzo, Raúl, Gavotti, Del, Godino, None
Roman, Burela, Pasupuleti, Piscoya, Vidal et al., Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clin Infect Dis,
doi:10.1101/2021.05.21.21257595Saini, Vago, None
Schneider, None
Segatori, Garona, Caligiuri, Bizzotto, Lavignolle et al., Effect of ivermectin and atorvastatin on nuclear localization of importin alpha and drug target expression profiling in host cells from nasopharyngeal swabs of SARS-CoV-2-positive patients, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v13102084Sepulveda, None
Siemieniuk, Bartoszko, Ge, Zeraatkar, Izcovich et al., Drug treatments for covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-Analysis, BMJ,
doi:10.1136/bmj.m2980Smit, Ochomo, Aljayyoussi, Kwambai, Abong et al., Safety and mosquitocidal efficacy of high-dose ivermectin when co-administered with dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine in Kenyan adults with uncomplicated malaria (IVERMAL): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Infect Dis,
doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30163-4Soledad, None
Solett, Rocío, None
Sosa, Bibiana Widemman, None
Sosa, Cepeda, None
Sosa, Schan, None
Stern, None
Suputtamongkol, Avirutnan, Mairiang, Angkasekwinai, Niwattayakul et al., Ivermectin accelerates circulating nonstructural protein 1 (NS1) clearance in adult dengue patients: a combined phase 2/3 randomized double-blinded placebo controlled trial, Clin Infect Dis an Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am,
doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1332Thompson, Stenehjem, Grannis, Ball, Naleway et al., Effectiveness of Covid-19 vaccines in ambulatory and inpatient care settings, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110362Thylefors, Alleman, Twum-Danso, Operational lessons from 20 years of the Mectizan Donation Program for the control of onchocerciasis, Trop Med Int Heal,
doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2008.02049.xTleyjeh, Kashour, Mandrekar, Petitti, Overlooked shortcomings of observational studies of interventions in coronavirus disease 2019: an illustrated review for the clinician, Open Forum Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab317Topfanini, Rovera, None
Torres, Anechi, None
Torres, Matías Altamira; María, Juri, Rosa, None
Torres, Muria, Gómez, None
Vallejos, Zoni, Bangher, Villamandos, Bobadilla et al., Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, BMC Infect Dis,
doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5Vanderberg, Dayana Iglesias; Maylen, Aimetta, None
Verdugo, None
Villagra, Barbero, Betina, None
Yoshida, Penego, None
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.813378",
"ISSN": [
"2296-2565"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.813378",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>In the absence of antiviral alternatives, interventions under research for COVID-19 might be offered following guidelines from WHO for monitored emergency use of unregistered and experimental interventions (MEURI). Ivermectin is among several drugs explored for its role against SARS-CoV-2, with a well-known safety profile but conflicting data regarding clinical utility for COVID-19. The aim of this report is to inform on the results of a MEURI Program of high-dose ivermectin in COVID-19 carried out by the Ministry of Health of the Province of La Pampa, Argentina.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>COVID-19 subjects, within 5 days of symptoms onset were invited to participate in the program, which consisted in the administration of ivermectin 0.6 mg/kg/day for 5 days plus standard of care. Active pharmacosurveillance was performed for 21 days, and hepatic laboratory assessments were performed in a subset of patients. Frequency of Intensive Care Unit (ICU) admission and COVID-19-related mortality of subjects in the ivermectin intention to treat group were compared with that observed in inhabitants of the same province during the same period not participating in the program.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>From 21,232 subjects with COVID-19, 3,266 were offered and agreed to participate in the ivermectin program and 17,966 did not and were considered as controls. A total of 567 participants reported 819 adverse events (AEs); 3.13% discontinued ivermectin due to adverse events. ICU admission was significantly lower in the ivermectin group compared to controls among participants ≥40 year-old (1.2 vs. 2.0%, odds ratio 0.608; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.024). Similarly, mortality was lower in the ivermectin group in the full group analysis (1.5 vs. 2.1%, odds ratio 0.720; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.029), as well as in subjects ≥ 40 year- old (2.7 vs. 4.1%, odds ratio 0.655; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.005).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>This report highlights the safety and possible efficacy of high dose ivermectin as a potentially useful intervention deserving public health-based consideration for COVID-19 patients.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fpubh.2022.813378"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayer",
"given": "Marcos Alejandro",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krolewiecki",
"given": "Alejandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferrero",
"given": "Alejandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bocchio",
"given": "Marcelo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barbero",
"given": "Juan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miguel",
"given": "Marcos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paladini",
"given": "Ariel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Delgado",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ojeda",
"given": "Juan Ramón",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elorza",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bertone",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fleitas",
"given": "Pedro Emanuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vera",
"given": "Gustavo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kohan",
"given": "Mario Rubén",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Frontiers in Public Health"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-22T05:37:46Z",
"timestamp": 1645508266000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-22T05:37:50Z",
"timestamp": 1645508270000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-22T06:11:54Z",
"timestamp": 1645510314479
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2296-2565"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
22
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1645488000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2022.813378/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"article-title": "A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B2",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Dashboard."
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7032e3",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in preventing hospitalization among adults aged ≥65 years - COVID-NET, 13 states, February-April (2021)",
"author": "Moline",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1088",
"journal-title": "Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2110362",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of Covid-19 vaccines in ambulatory and inpatient care settings",
"author": "Thompson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1355",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01967-X",
"article-title": "The long road ahead for COVID-19 vaccination in Africa",
"author": "Jerving",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "827",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "398",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "B6",
"unstructured": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m2980",
"article-title": "Drug treatments for covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-Analysis",
"author": "Siemieniuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m2980",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B8",
"unstructured": "Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pt.2014.07.005",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: panacea for resource-poor communities?",
"author": "Omura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "445",
"journal-title": "Trends Parasitol.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-3156.2008.02049.x",
"article-title": "Operational lessons from 20 years of the Mectizan Donation Program for the control of onchocerciasis",
"author": "Thylefors",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "689",
"journal-title": "Trop Med Int Heal.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pt.2017.02.004",
"article-title": "Ivermectin – old drug, new tricks?",
"author": "Laing",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "463",
"journal-title": "Trends Parasitol.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1332",
"article-title": "Ivermectin accelerates circulating nonstructural protein 1 (NS1) clearance in adult dengue patients: a combined phase 2/3 randomized double-blinded placebo controlled trial",
"author": "Suputtamongkol",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e586",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis an Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antivir Res.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of ivermectin in the treatment of COVID-19: a trial sequential analysis highlighted the requirement of additional randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Padhi",
"key": "B14",
"volume-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3071",
"article-title": "Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "López-Medina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1426",
"journal-title": "J Am Med Assoc.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5",
"article-title": "Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Vallejos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: a proof-of-concept randomized trial",
"author": "Krolewiecki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e100959",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001442",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines",
"author": "Bryant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e434",
"journal-title": "Am J Ther.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.05.31.21258081",
"article-title": "Favorable outcome on viral load and culture viability using Ivermectin in early treatment of non-hospitalized patients with mild COVID-19 – A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Biber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "B19",
"volume-title": "medRxiv",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720",
"article-title": "The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Chaccour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100720",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Ethical issues related to study design for trials on therapeutics for Ebola Virus Disease",
"first-page": "1",
"key": "B21",
"volume-title": "WHO Ethics Work Gr Meet",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aohep.2021.100321",
"article-title": "Drug-induced liver injury: a management position paper from the Latin American Association for Study of the liver",
"author": "Bessone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100321",
"journal-title": "Ann Hepatol.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkz524",
"article-title": "Safety of high-dose ivermectin: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Navarro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "827",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30163-4",
"article-title": "Safety and mosquitocidal efficacy of high-dose ivermectin when co-administered with dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine in Kenyan adults with uncomplicated malaria (IVERMAL): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Smit",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "615",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab365",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of albendazole and high-dose ivermectin co-administration in schoolaged children infected with Trichuris trichiura in Honduras: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Matamoros",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1203",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF00637608",
"article-title": "The relative systemic availability of ivermectin after administration as capsule, tablet, and oral solution",
"author": "Edwards",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "681",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Pharmacol.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "35",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab394",
"article-title": "Expression of concern: “meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Hill",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "ofab394",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.05.21.21257595",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Roman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "B28",
"volume-title": "Clin Infect Dis.",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001450",
"article-title": "Bayesian hypothesis testing and hierarchical modeling of ivermectin effectiveness",
"author": "Neil",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "CD015017",
"journal-title": "Am J Ther.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13102084",
"article-title": "Effect of ivermectin and atorvastatin on nuclear localization of importin alpha and drug target expression profiling in host cells from nasopharyngeal swabs of SARS-CoV-2- positive patients",
"author": "Segatori",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2084",
"journal-title": "Viruses.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen",
"author": "Heidary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "J Antibiot.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0031182005009108",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory effect of various anti-parasitics: a review",
"author": "Sajid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "301",
"journal-title": "Parasitology.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.115.108399",
"article-title": "It's the context! Am J Clin Nutr",
"author": "Manary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001441",
"article-title": "Pitfalls in reporting sample size calculation across randomized controlled trials involving ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e616",
"journal-title": "Am J Ther.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1037/a0024338",
"article-title": "Effect size estimates: current use, calculations, and interpretation",
"author": "Fritz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "J Exp Psychol Gen.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab317",
"article-title": "Overlooked shortcomings of observational studies of interventions in coronavirus disease 2019: an illustrated review for the clinician",
"author": "Tleyjeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis.",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 36,
"references-count": 36,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Front. Public Health"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Safety and Efficacy of a MEURI Program for the Use of High Dose Ivermectin in COVID-19 Patients"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "10"
}